As I mentioned in the last post, things seem to be looking up for the sage-grouse. So what about our research?

Lots of sage-grouse watching again this year

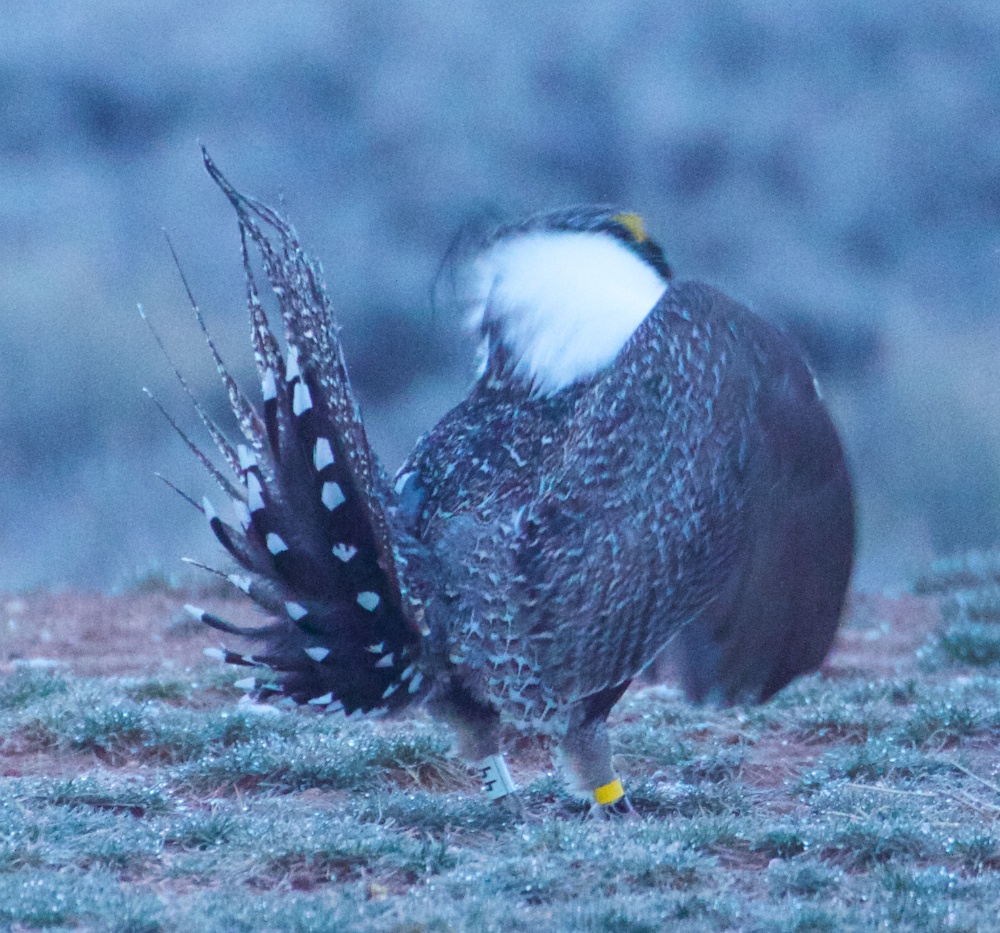
A burrowing owl looks in on the sage-grouse lek
We stuck with the same two focal leks that we used last year, Chugwater and Cottontail. Basic monitoring went well, especially with the increasing number of banded birds making it a little easier to get ID’s on the lek, especially in windy weather. We came back with a great set of video and audio data. What is particularly nice is that we can now look at lekking behavior in an increasing population. We now have a lot of recordings from “bad” years in which the population was declining, so seeing how hard males work and what females do in a “good” year, a year with lots of young males on the lek and possibly better overwinter survival, could make a nice contrast when we start to examine the long-term trends in display and mate choice.
 The first of our main goals was to continue with our robot experiments. This year, our goal was to try the “outside option” experiment again. We first tried this in 2013, but our additional robots “Salt” and “Pepa” were not constructed until fairly late in the season that year. We started a few trials, but the males were already winding down their display effort and were not responsive enough to warrant trying a new series. Turn to 2015, and we now have our robots ready! Credit to Anna Perry, who devised the first protocol, Ryane, who took the reins this year as experiment planner and main robot director, and of course Gail who put the robots together and has been working with robot birds for a long time.
The first of our main goals was to continue with our robot experiments. This year, our goal was to try the “outside option” experiment again. We first tried this in 2013, but our additional robots “Salt” and “Pepa” were not constructed until fairly late in the season that year. We started a few trials, but the males were already winding down their display effort and were not responsive enough to warrant trying a new series. Turn to 2015, and we now have our robots ready! Credit to Anna Perry, who devised the first protocol, Ryane, who took the reins this year as experiment planner and main robot director, and of course Gail who put the robots together and has been working with robot birds for a long time.
So what was the experiment? Briefly, there’s a principal from the economic literature that while negotiations and haggling often occur in one-on-one situations, the broader market includes lots of different options and competitors for both buyers and sellers, and the presence of these “outside options” can make a big difference in the decisions that are made in the market. In particular, if a seller is engaging with one buyer who is not terribly eager to buy, the seller might benefit from switching to a new buyer, but only if the new buyer seems more profitable or eager than the original trading partner.
We wanted to test this with the sage-grouse, using two fembots as potential “buyers”, and treating the male sage-grouse as sellers. We were able to get trials on each lek where the outside option was either “interested” or “disinterested”. We also ran control trials throughout the season with only a single robot- these will help us correct for seasonal changes in how hard the males work (they seem to get tired towards the end of the season).

A successful night
Our second main goal was to gather a lot of movement and foraging data, so we can uncover the feedbacks between on-lek display behavior and off-lek foraging behavior of the males. This was moderately successful. The first step was catching males and putting on encounternet transmitters. These are small solar-powered devices that can log both where the male is and also capture data about how it is moving it’s body. We managed to get around 20 tags deployed, although we were hoping for more. The tall grass, while great for the birds in providing cover from predators, may have made it more difficult to see the eyeshine at night during our spotlighting forays. Additionally, the age ratio of the growing population meant there were more young males to be caught, and not all of those males set up territories on the lek.

Downloading encounternet data
All in all, we collected tracking data from 7 males, which when combined with the 4 males from last year, should give us a good picture of where males go off the lek and how they spend their time. For these 7 males, we used the positional GPS data to go out and find their foraging and roosting spots, and measure aspects of the habitat at these locations to learn more about how male sage-grouse use the landscape. We also took small clippings of the sagebrush to see how selective they might be in what they are eating.
One new pilot project this year, we collected some poop from the leks to check for the presence of a certain type of gut parasite called coccidia. If sage-grouse have a lot of it, it could be an important factor in explaining differences in behavior. There’s also the possibility that the toxins in the sage are strong enough to limit this type of parasite. Dr. Rich Buchholz at the University of Mississippi has agreed to look through our samples and give us an idea of what we are working with.
Many thanks to our crew this year Amber, John, Miles, McKinzie, and Kelly for their help this year! Also thanks for the help from the Boise State crew, in particular Chelsea and Marcella who stayed at Chicken Camp for several weeks helping catch birds and organize the vegetation sampling. Also thanks to Sue Oberlie (BLM) and Stan Harter (WyoG&F) for local institutional support and a number of people who stepped in once to help capture sage-grouse. We couldn’t have done it without you all!

The 2015 Crew
In the next post I’ll talk about outreach and other odds and ends of the season.